Industrial Robot Safety Standards and Best Practices for Employers and Workers
The integration of industrial robots into the workplace has revolutionized manufacturing and production processes, enhancing efficiency and productivity. However, this advancement comes with significant safety considerations that employers and workers must address. This article will explore the key safety hazards associated with industrial robots, the relevant safety standards and regulations, and best practices for ensuring a safe working environment. By understanding these elements, employers can mitigate risks and protect their workforce effectively. We will also discuss the importance of training and certification in maintaining safety standards and how emerging technologies can further enhance safety measures.
What Are the Key Safety Hazards in Industrial Robot Workplaces?
Industrial robots, while beneficial, pose several safety hazards that must be recognized and managed. Understanding these hazards is crucial for creating a safe working environment.
Which Common Hazards Should Employers and Workers Recognize?

Common hazards in robotic workplaces include mechanical risks, electrical hazards, and human-robot interaction issues. Mechanical risks arise from the robot’s moving parts, which can cause injuries if workers are in close proximity during operation. Electrical hazards can occur due to improper wiring or maintenance, leading to shocks or equipment failures. Additionally, human-robot interaction can lead to accidents if workers are not adequately trained to work alongside robots. Recognizing these hazards is the first step in implementing effective safety measures.
How Does Human Error Impact Robot Safety?
Human error significantly impacts robot safety, often leading to accidents and injuries. Studies indicate that a substantial percentage of workplace incidents involving robots are attributed to human mistakes, such as improper programming or failure to follow safety protocols. Preventive measures, including comprehensive training and clear operational guidelines, can help reduce the likelihood of human error. By fostering a culture of safety awareness, employers can enhance the overall safety of robotic work environments.
What Industrial Robot Safety Standards and Regulations Must Be Followed?
Compliance with safety standards and regulations is essential for ensuring the safe operation of industrial robots. Employers must be aware of the relevant guidelines to maintain a safe workplace.
How Do OSHA Guidelines and the General Duty Clause Apply to Robot Safety?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides guidelines that are critical for robot safety. The General Duty Clause requires employers to provide a workplace free from recognized hazards. This means that employers must assess the risks associated with robotic operations and implement necessary safety measures. Failure to comply with OSHA regulations can result in severe penalties and increased liability in the event of an accident.
What Are the Roles of ANSI/RIA R15.06 and ISO 10218 in Robot Safety Compliance?
ANSI/RIA R15.06 and ISO 10218 are key standards that govern robot safety compliance. ANSI/RIA R15.06 outlines safety requirements for industrial robots, including risk assessment and safety measures for robot design and operation. ISO 10218 complements these guidelines by providing international standards for robot safety, ensuring that manufacturers and employers adhere to best practices. Compliance with these standards not only enhances safety but also promotes a culture of responsibility within the workplace.
Further emphasizing the critical role of these guidelines, the current industrial robot safety standard is a national adoption of international benchmarks.
Industrial Robot Safety Standards: ANSI/RIA & ISO Compliance
The current version of the Industrial Robot Safety Standard, ANSI/RIA R15. 06-2012, is a US national adoption of the ISO 10218-2011, Part 1, Robots, and Part 2, Robotic. TS 15066:2016 on collaborative robot safety is an example of a key standard. Ensuring the robot system is in compliance with these standards is crucial. … current version of the Industrial Robot Safety Standard, ANSI/RIA R15. 06-2012, is a US national adoption of the ISO 10218-2011, Part 1, Robots, and Part 2, Robotic …, 2012
How Can Employers Implement Effective Safeguards for Robotic Work Cells?
Employers must take proactive steps to implement effective safeguards in robotic work cells to protect their workforce.
What Engineering Controls Protect Workers from Robot Hazards?
Engineering controls are essential for minimizing risks associated with robotic operations. These controls include physical barriers, such as safety cages or light curtains, that prevent unauthorized access to robot work areas. Additionally, implementing emergency stop buttons and safety interlocks can help mitigate risks during unexpected situations. By investing in these engineering controls, employers can significantly enhance worker safety.
Which Administrative Controls and PPE Are Essential for Robot Safety?
Administrative controls and personal protective equipment (PPE) play a vital role in ensuring safety in robotic environments. Administrative controls include establishing clear operational procedures, conducting regular safety audits, and providing ongoing training for workers. PPE, such as safety glasses, gloves, and hard hats, is also crucial for protecting workers from potential hazards. Together, these measures create a comprehensive safety strategy that addresses both engineering and human factors.
What Are the Best Practices for Lockout Tagout Procedures in Robotics?
Lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures are critical for ensuring safety during maintenance and servicing of robotic systems. Proper implementation of these procedures can prevent accidental machine start-up and protect workers from injury.
How Is Lockout Tagout Applied Specifically to Industrial Robots?
Lockout/tagout procedures for industrial robots involve specific steps to ensure that machines are properly shut down and cannot be restarted while maintenance is performed. This includes identifying all energy sources, isolating them, and applying lockout devices to prevent accidental re-energization. Training workers on these procedures is essential to ensure compliance and safety during maintenance activities.
What OSHA Standards Govern Lockout Tagout for Robotic Systems?
OSHA has established standards that govern lockout/tagout procedures, specifically 29 CFR 1910.147. These standards require employers to develop and implement an energy control program that includes training, procedures, and audits. Compliance with these standards not only protects workers but also reduces the risk of costly accidents and downtime.
OSHA continues to review and potentially update its lockout/tagout standards to address the evolving landscape of robotics.
OSHA Lockout/Tagout for Robotic Safety
OSHA may also consider changes to the lockout/tagout standard that address hazardous energy control for new robotics. Using Machine Safety Risk Assessment for Alternative Methods to LOCKOUT/TAGOUT, 1910
Why Is Training and Certification Critical for Industrial Robot Safety?
Industrial Robot Safety Training and Certification are fundamental components of a robust safety program in environments with industrial robots. Proper training ensures that workers understand the risks and safety protocols associated with robotic operations.
Which Roles Require Specialized Robot Safety Training?
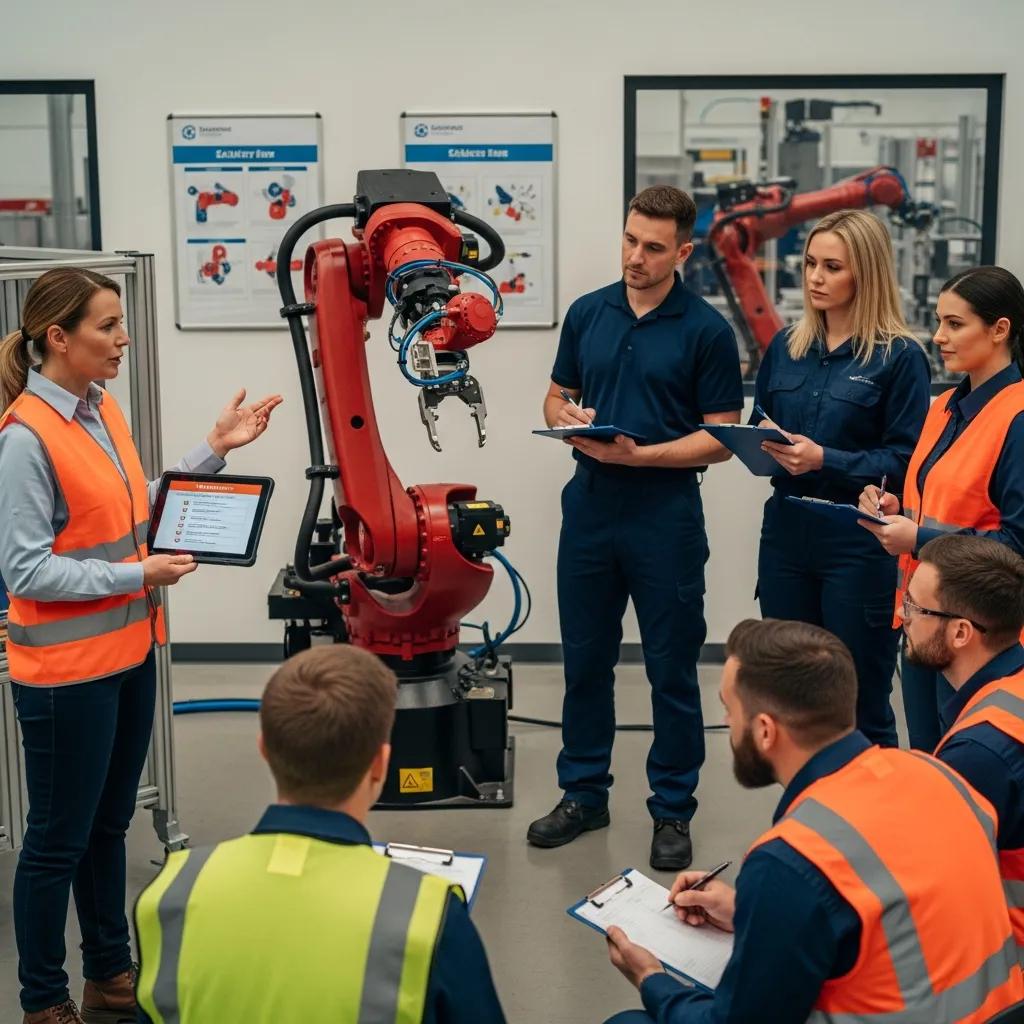

Certain roles within an organization require specialized training to ensure safety when working with industrial robots. Operators, maintenance personnel, and safety officers should receive comprehensive training that covers robot operation, emergency procedures, and safety standards. This specialized training equips employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to work safely alongside robotic systems.
How Does Laser Safety Expertise Enhance Industrial Robot Safety Programs?
Laser safety expertise is particularly relevant in environments where industrial robots are used for laser applications. Understanding laser safety protocols can significantly enhance overall safety programs by addressing specific risks associated with laser operations. Training in laser safety ensures that workers are aware of potential hazards and know how to mitigate them effectively.
How Can Risk Assessment and Emerging Technologies Improve Robot Safety?
Conducting thorough risk assessments and leveraging emerging technologies are essential for enhancing safety in robotic environments.
What Steps Are Involved in Conducting a Robot Safety Risk Assessment?
A comprehensive robot safety risk assessment involves several key steps. First, employers must identify potential hazards associated with robotic operations. Next, they should evaluate the risks and determine the likelihood and severity of potential incidents. Finally, implementing appropriate control measures and regularly reviewing the assessment ensures ongoing safety. This proactive approach helps organizations stay ahead of potential safety issues.
How Do AI and Predictive Maintenance Influence Future Robot Safety Measures?
Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive maintenance, are transforming safety measures in robotic environments. AI can analyze data from robotic systems to identify patterns and predict potential failures before they occur. Predictive maintenance allows organizations to address issues proactively, reducing the likelihood of accidents and enhancing overall safety. By integrating these technologies, employers can create a safer and more efficient workplace.
| Safety Aspect | Description | Importance |
| Mechanical Risks | Hazards from moving parts of robots | High |
| Electrical Hazards | Risks from improper wiring or faults | Medium |
| Human-Robot Interaction | Accidents due to lack of training | High |
Employers must prioritize safety in robotic workplaces by recognizing hazards, adhering to safety standards, and implementing effective training programs. By fostering a culture of safety and leveraging emerging technologies, organizations can protect their workforce and enhance operational efficiency.
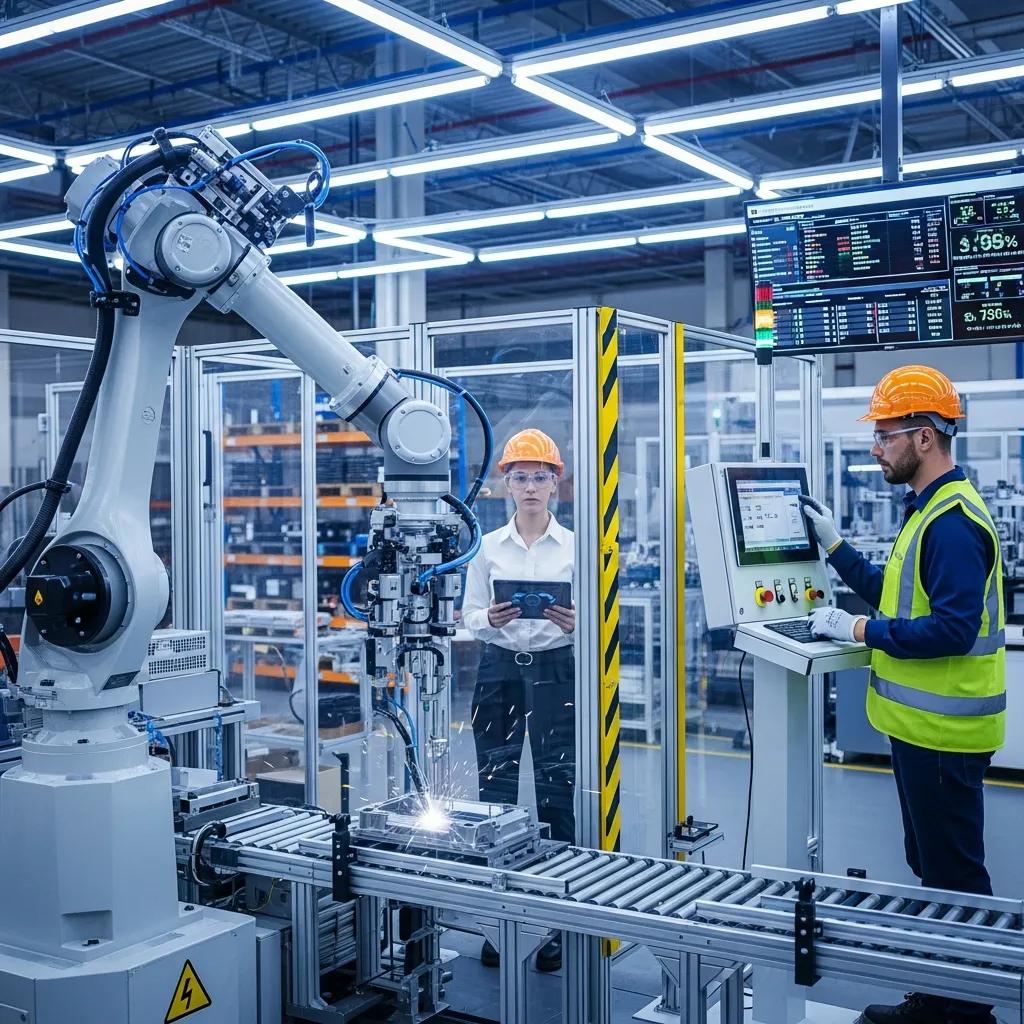




One aspect that stood out to me was how emerging technologies can help improve safety in the workplace. Whether it’s through better robot programming or more advanced sensors, technology has the potential to prevent many of the hazards mentioned.